Organisation : Jamabandi (Haryana Land Record Documents)
Facility Name : Check Mutation of Deed and Raise Objection
Applicable State/UT : Haryana
Website : https://jamabandi.nic.in/DefaultPages/Default
How To Check Mutation of Deed in Haryana?
To check Mutation of Deed and Raise Objection in Haryana, Follow the below steps
Related / Similar Facility : Haryana Jamabandi Khewat/ Khatoni Details Online
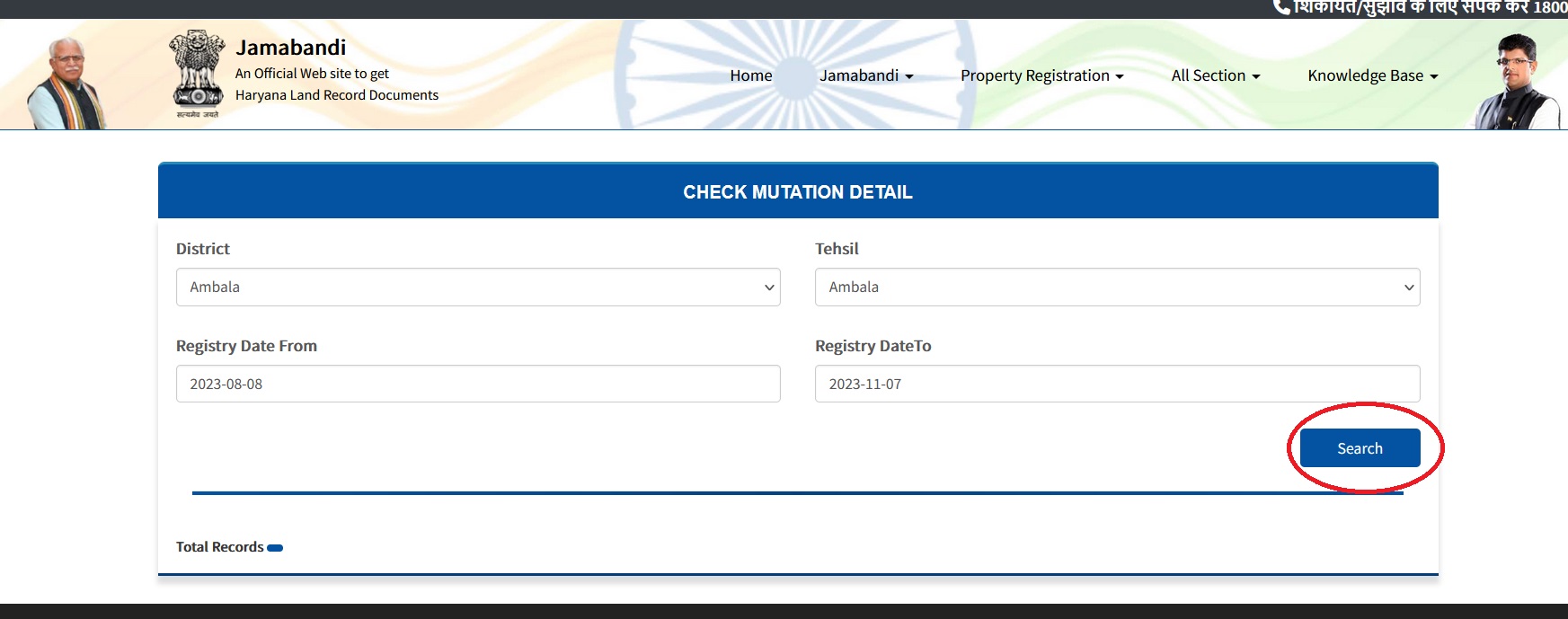
Steps:
Step-1 : Go to the link https://jamabandi.nic.in/DSNakal/CheckMutDetail1
Step-2 : Select the District, Tehsil, Registry Date
Step-3 : Click On Search Button

There are two primary ways to check the mutation of a deed in Haryana:
1. Online through the Jamabandi portal:
1. Go to the Jamabandi website.
2. Click on the “Mutation” tab.
3. Select “View Mutation” option.
4. Enter the following details:
** Tehsil (Taluk)
** Village
** Mutation number (if known)
** Source type (e.g., sale, inheritance)
** Mutation type (e.g., new entry, deletion)
** Mutation date (if known)
5. Enter the captcha code and click “Submit.”
6. The system will display the details of the mutation, including the parties involved, date of transaction, and updated ownership information.
2. Offline through the Tehsildar office:
** Visit: The Tehsildar office for your district.
** Documents: Carry copies of the deed and any other relevant documents.
** Process: The Tehsildar or their staff can access the mutation records and provide you with information about the transaction.
FAQ On Jamabandi Haryana
Frequently Asked Questions FAQ On Jamabandi Haryana
Whether the executant is bound to pay stamp duty and registration fee on the value of the Collector’s rate?
Executant is not bound to pay stamp duty and registration fee on the value of the Collector’s rate. He can refer his case to the Collector under Section 47-A of the Indian Stamp Act, 1899 for determination of the value of consideration and proper amount of stamp duty and registration fee payable therein.
Who are called Collectors and Appellate Authority U/S 47A of the Indian Stamp Act, 1899?
Deputy Commissioners, SDOs(C) and District Revenue Officers are declared as Collectors under Section 47-A of the Indian Stamp Act, 1899. The Divisional Commissioners are declared as Appellate Authority under this Act.
In the case of sale deed, conveyance deed, exchange deed, lease/rent deed, partition deeds by whom stamp duty has to be paid?
Purchaser has to pay stamp duty on sale/conveyance deeds. In the case of exchange deeds, both the parties have to pay stamp duty in equal shares. In lease/rent deed, it is payabvle by the lessee. In partition deeds it is payable by the parties in proportion to their respective shares. In all other cases, the stamp duty is generally payable by the executant of the documents.
Name the main documents which are compulsorily registrable documents and under which section of the Act.
Mainly all documents relating to sale, conveyance, exchange, gift, settlement partition, mortgage, lease, decrees and release of immovable property of the value of one hundred rupees or more are compulsorily registerable documents under Section 17 of the Registration Act, 1908. The remaining categories of documents as mentioned in Section 18 of the Registration Act, 1908 are optionally registerable documents.
Is a power of attorney compulsorily registerable document?
Power of Attorney is not a compulsorily registerable document.
In the recent past agreements of sale have been made compulsorily registerable documents. Can these be treated as a title deed?
Agreement of sale cannot be treated as a title deed. However, this will give a right to its holder to obtain a sale deed in his favour. Registration will enhance its evidentiary value and credibility.
When a document is reliable to be stamped?
All documents chargeable with duty and executed in India shall be stamped before or at the time of execution (Section 17 of the Indian Stamp Act, 1899).